Get The Mindmap We Used To Generate 13.2 Million Visits To A Single Brand With Zero Ad-Spend
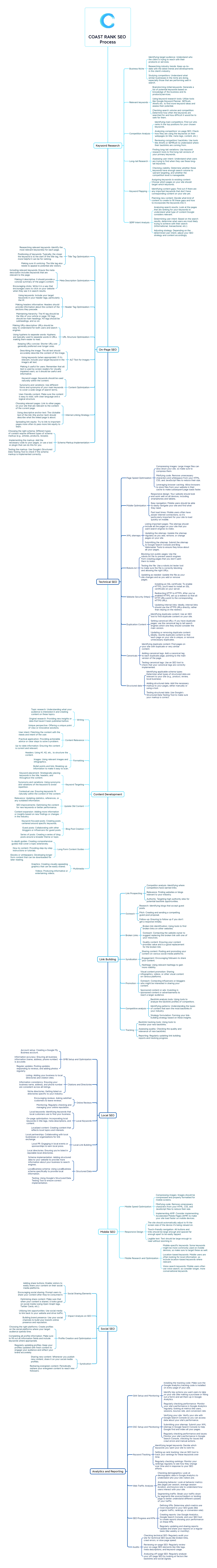
The SEO Mind Map
Keyword Research
Business Niche
Identifying target audience: Understand who the client is trying to reach with their products or services.
Researching industry trends: Keep up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in the client’s industry.
Studying competitors: Understand what similar businesses in the niche are doing, especially those that are performing well in search.
Relevant keywords
Brainstorming initial keywords: Generate a list of potential keywords based on knowledge of the business and its products/services.
Using keyword research tools: Utilize tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, Ahrefs etc. to find more keyword ideas and assess their potential.
Checking search volume and competition: Determine how often the keywords are searched for and how difficult it would be to rank for them.
Competition Analysis
Identifying main competitors: Find out who ranks in the top positions for your chosen keywords.
Analyzing competitors’ on-page SEO: Check how they are using the keywords on their webpages (in title, meta tags, content, etc.).
Reviewing competitors’ backlinks: Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMRush to understand where their backlinks are coming from.
Long-tail Research
Finding long-tail variations: Use keyword research tools to find long-tail versions of your primary keywords.
Assessing user intent: Understand what users are trying to find when they use these long-tail keywords.
Checking viability: Determine whether these keywords have enough search volume to warrant targeting, and whether the competition level is manageable.
Keyword Mapping
Assigning keywords to existing content: Choose which pages on your site should target which keywords.
Identifying content gaps: Find out if there are any important keywords that don’t have corresponding content on your site yet.
Planning new content: Decide what kind of content to create to fill these gaps and how to incorporate the keywords into it.
SERP Intent Analysis
Analyzing search results: Look at the pages that are ranking for your keywords to understand what type of content Google considers relevant.
Determining user intent: Based on the search results, determine what users are most likely trying to achieve with their search (informational, transactional, etc.).
Adjusting strategy: Depending on the determined user intent, adjust your SEO strategy and content accordingly.
On-Page SEO
Title Tag Optimization
Researching relevant keywords: Identify the most relevant keyword(s) for each page.
Positioning of keywords: Typically, the closer the keyword is to the start of the title tag, the more helpful it can be for ranking.
Making sure it’s enticing: The title tag also needs to appeal to potential site visitors.
Meta Description Optimization
Including relevant keywords: Ensure the meta description includes keywords that are relevant to the page.
Making it descriptive: It should provide a concise summary of the page’s content.
Encouraging clicks: Write it in a way that encourages users to click on your website when they see it in search results.
Header Tag Optimization
Using keywords: Include your target keywords in your header tags, particularly the h2.
Making headers informative: Headers should provide information about the content of the sections they precede.
Maintaining hierarchy: The h2 tag should be the title of your article or page, h3 tags should be main headings, br tags should be subheadings, and so on.
URL Structure Optimization
Making URLs descriptive: URLs should be easy to understand for both users and search engines.
Using hyphens to separate words: Hyphens are typically used to separate words in URLs, making them easier to read.
Keeping URLs concise: Shorter URLs are generally preferred over longer ones.
ALT Text for Images
Describing the image: The alt text should accurately describe the content of the image.
Using keywords (when appropriate): If it’s relevant, include your target keyword in the image’s alt text.
Making it useful for users: Remember that alt text is used by screen readers for visually impaired users, so it should be useful and informative.
Content Optimization
Keyword usage: Keywords should be used naturally within the content.
Synonyms and variations: Use different forms and synonyms of your main keywords to cover a wide range of search terms.
User-friendly content: Make sure the content is easy to read, with clear language and a logical structure.
Internal Linking Strategy
Choosing relevant pages: Link to other pages on your site that are relevant to the content of the current page.
Using descriptive anchor text: The clickable text of the link (the anchor text) should describe what the linked page is about.
Spreading link equity: Try to link to important pages more often to pass more link equity to them.
Schema Markup Implementation
Choosing the right schema: Different types of content require different types of schema markup (e.g., articles, products, recipes).
Implementing the markup: Add the necessary code to your pages, or use a tool or plugin that can do this for you.
Testing the markup: Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to check if the schema markup is implemented correctly.
Technical SEO
Page Speed Optimization
Compressing images: Large image files can slow down your site, so make sure to compress them.
Minifying code: Remove unnecessary characters and whitespace from your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files to reduce their size.
Leveraging browser caching: Allow browsers to store files from your website in their cache to make subsequent page loads faster.
Mobile Optimization
Responsive design: Your website should look and work well on all devices, including smartphones and tablets.
Easy navigation: Mobile users should be able to easily navigate your site and find what they need.
Fast load times: Mobile users often have slower internet connections, so it’s particularly important for your site to load quickly on mobile.
XML sitemaps
Listing important pages: The sitemap should include all the pages on your site that you want search engines to index.
Updating the sitemap: Update the sitemap regularly as you add, remove, or change pages on your site.
Submitting the sitemap: Submit the sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to ensure they know about all your pages.
Robots.txt
Blocking non-public pages: Use the robots.txt file to prevent search engines from crawling pages that you don’t want them to index.
Testing the file: Use a robots.txt tester tool to make sure the file is correctly blocking and allowing the right URLs.
Updating as needed: Update the file as your site changes and as you add or remove pages.
Website Security (https)
Installing an SSL certificate: To enable HTTPS, you’ll need to install an SSL certificate on your server.
Redirecting HTTP to HTTPS: After you’ve enabled HTTPS, set up a redirect so that all HTTP URLs point to the corresponding HTTPS URLs.
Updating internal links: Ideally, internal links should use the HTTPS URLs directly, rather than relying on the redirect.
Duplication Content
Identifying duplicate content: Use an SEO tool to find duplicate content on your site.
Setting canonical URLs: If you have duplicate pages, use the canonical tag to tell search engines which one they should consider the main version.
Updating or removing duplicate content: Ideally, rewrite duplicate content so that each page on your site is unique, or remove unnecessary duplicates.
Canonicals
Identifying duplicate content: Find pages on your site with duplicate or very similar content.
Adding canonical tags: Add a canonical tag to each duplicate page, pointing to the main version of the page.
Testing canonical tags: Use an SEO tool to check that your canonical tags are correctly implemented.
Structured data
Identifying applicable schema types: Determine what types of structured data are relevant to your site (e.g., product, review, local business).
Adding structured data: Add the necessary markup to your pages, either manually or using a tool.
Testing structured data: Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to make sure your markup is correct.
Content Development
Writing
Topic research: Understanding what your audience is interested in and creating content on these topics.
Original research: Providing new insights or data that haven’t been published before.
Unique perspective: Offering a unique point of view or innovative solutions.
Content Relevance
User intent: Matching the content with the needs and intent of the user.
Practical application: Providing actionable advice or clear steps to solve a problem.
Up-to-date information: Ensuring the content is current and relevant.
Formatting
Headers: Using h2, h3, etc., to structure the content.
Images: Using relevant images and infographics.
Bullet points and lists: Breaking up information to make it easy to scan.
Keyword Targeting
Keyword placement: Strategically placing keywords in the title, headers, and throughout the content.
Synonyms and variations: Using synonyms and variations of the keyword to avoid repetition.
Contextual use: Ensuring keywords fit naturally within the context of the content.
Update Old Content
Relevance: Updating statistics, references, or any outdated information.
SEO improvements: Optimizing the content for new keywords or better performance.
Content expansion: Adding more information or insights based on new findings or changes in the industry.
Blog Post Creation
Keyword-focused posts: Creating posts centered around specific keywords.
Guest posts: Collaborating with other bloggers or influencers for guest posts.
Series of posts: Creating a series of blog posts around a broader theme or topic.
Long Form Content Guides
In-depth guides: Creating comprehensive guides that cover a topic extensively.
How-to content: Providing step-by-step instructions or tutorials.
Ebooks or whitepapers: Developing longer form content that can be downloaded for later reading.
Multimedia
Graphics: Creating visually appealing graphics that can be easily shared.
Videos: Producing informative or entertaining videos.
Link Building
Link Prospecting
Competitor analysis: Identifying where competitors have earned links.
Relevance: Finding websites or blogs relevant to your industry.
Authority: Targeting high-authority sites for potential backlink opportunities.
Outreach
Research: Identifying blogs that accept guest posts.
Pitch: Creating and sending a compelling guest post proposal.
Follow-up: Ensuring to follow up if you don’t get a response initially.
Broken Links
Broken link identification: Using tools to find broken links on other websites.
Outreach: Contacting the website owner to suggest replacing the broken link with one of your resources.
Quality content: Ensuring your content provides value and is a good replacement for the broken link.
Syndication
Sharing content: Posting and promoting your content on various social media platforms.
Engagement: Encouraging followers to share your content.
Hashtags: Using relevant hashtags to gain more visibility.
Promotion
Visual content promotion: Sharing infographics, videos, or other visual content on various platforms.
Outreach: Contacting influencers or bloggers who might be interested in sharing your content.
Sponsored content or ads: Investing in sponsored content or advertisements to reach a larger audience.
Competitive analysis
Backlink analysis tools: Using tools to analyze the backlink profiles of competitors.
Identifying patterns: Understanding the types of content that earn the most backlinks in your industry.
Strategy formulation: Forming your link-building strategy based on these insights.
Tracking
Backlink tracking tools: Using tools to monitor your new backlinks.
Assessing quality: Checking the quality and relevance of new backlinks.
Reporting: Regularly updating link building reports and tracking progress.
Local SEO
GMB Setup and Optimization
Account setup: Creating a Google My Business account.
Information accuracy: Ensuring all business information (name, address, phone number) is accurate.
Regular updates: Posting updates, responding to reviews, and adding photos regularly.
Citations and Directories
Listing: Adding your business to local directories and citation sites.
Information consistency: Ensuring your business name, address, and phone number are consistent across all listings.
Niche directories: Getting listed on directories specific to your industry.
Online Reviews
Encouraging reviews: Asking satisfied customers to leave reviews.
Monitoring: Regularly checking and managing your online reputation.
Local Keywords
Local keywords: Identifying keywords that local customers use to find your business.
On-page optimization: Incorporating local keywords in title tags, meta descriptions, and content.
Localized content: Creating content that reflects local topics and interests.
Local Link Building
Local partnerships: Collaborating with local businesses or organizations for link exchange.
Local PR: Engaging in local events or sponsorships to earn local press.
Local directories: Ensuring you’re listed in reputable local directories.
Structured Data
Schema implementation: Adding structured data to your website to provide more information about your business to search engines.
LocalBusiness schema: Using LocalBusiness schema specifically to provide local information.
Testing: Using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to ensure correct implementation.
Mobile SEO
Mobile Speed Optimization
Compressing images: Images should be compressed and properly formatted for mobile screens.
Minifying code: Remove unnecessary characters from your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files to reduce their size.
Implementing AMP: Consider implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) to make your site load faster on mobile devices.
Responsive Design
The site should automatically adjust to fit the screen size of the device it’s being viewed on.
Touch-friendly navigation: All buttons and links should be large enough and spaced far enough apart to be easily tapped.
Legible text: Text should be large enough to read without zooming in.
Mobile Research and Optimization
Mobile-specific keywords: Some keywords might be more commonly used on mobile devices, so make sure to target these as well.
Location-based keywords: Mobile users are often looking for local information, so include location-based keywords where relevant.
Voice search keywords: Mobile users often use voice search, so consider longer, more conversational keywords.
Social SEO
Social Sharing Elements
Adding share buttons: Enable visitors to easily share your content on their social media platforms.
Encouraging social sharing: Prompt users to share your content after they’ve consumed it.
Optimizing share content: Make sure that when your content is shared, it looks good on social media (using Open Graph tags, Twitter Cards, etc.).
Impact Analysis on SEO
Utilizing link opportunities: Use social media to link back to your website and drive traffic.
Building brand presence: Use your social channels to build your brand’s online presence and reputation.
Profile Creation and Optimization
Choosing the right platforms: Create profiles on the social platforms where your target audience spends time.
Completing all profile information: Make sure to fill out all information fields and include keywords where appropriate.
Regularly updating profiles: Keep your profiles updated with fresh content to engage your audience and reflect your brand accurately.
Syndication
Sharing new content: Whenever you publish new content, share it on your social media profiles.
Resharing evergreen content: Periodically reshare your evergreen content to reach new followers.
Analytics and Reporting
GA4 Setup and Monitoring
Installing the tracking code: Make sure the Google Analytics tracking code is installed on every page of your site.
Identify key actions you want users to take on your site (like making a purchase or filling out a form) and set them up in Google Analytics.
Regularly checking performance: Monitor your site’s performance in Google Analytics regularly, looking at metrics like users, sessions, bounce rate, and conversion rate.
GSC Setup and Monitoring
Verifying your site: Verify your site with Google Search Console so you can access data about your site’s performance.
Submitting your sitemap: Submit your XML sitemap in Google Search Console to help Google find and index all your pages.
Regularly checking performance and issues: Monitor your site’s performance in Google Search Console, checking for issues like crawl errors and manual actions.
Keyword Tracking
Identifying target keywords: Decide which keywords you want your site to rank for.
Setting up rank tracking: Use an SEO tool to track your rankings for these keywords over time.
Regularly checking rankings: Monitor your rankings regularly to see how they change over time and in response to your SEO efforts.
Web Traffic Analysis
Checking demographics: Look at demographic data in Google Analytics to understand who your site visitors are.
Analyzing behavior: Look at behavior metrics like pages per session, average session duration, and bounce rate to understand how users interact with your site.
Segmenting traffic: Break your traffic down by segments like source/medium or landing page to better understand different subsets of your traffic.
SEO Progress and KPIs
Defining KPIs: Determine which metrics are most important to your SEO goals (like organic traffic, rankings, or conversion rate).
Creating reports: Use Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and your SEO tool to create reports showing your performance on these KPIs.
Regularly updating and sharing reports: Update and share your reports on a regular basis (like weekly or monthly).
Audits
Checking technical SEO: Regularly audit your site for technical SEO issues like broken links, crawl errors, or slow page speed.
Reviewing on-page SEO: Regularly review your on-page SEO elements like title tags, meta descriptions, and keyword usage.
Analyzing off-page SEO: Regularly analyze your off-page SEO by looking at factors like backlinks and social signals.
